
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that stores the record of ownership of digital assets. Any data stored on blockchain is unable to be modified, making the technology a legitimate disruptor for industries like payments, cybersecurity and healthcare. Discover more on what it is, how it’s used and its history.
BLOCKCHAIN Technology
BLOCKCHAIN MEANING: BLOCKCHAIN EXPLAINED
-
A blockchain is a digital ledger or database where encrypted blocks of digital asset data are stored and chained together, forming a chronological single-source-of-truth for the data.
-
Digital assets are distributed, not copied or transferred.
-
Digital assets are decentralized, allowing for real-time accessibility, transparency and governance amongst more than one party.
-
Blockchain ledgers are transparent — any changes made are documented, preserving integrity and trust.
-
Blockchain ledgers are public and constructed with inherent security measures, making it a prime technology for almost every sector.
Why Is Blockchain Important?
Popularized by its association with cryptocurrency and NFTs, blockchain technology has since evolved to become a management solution for all types of global industries. Today, you can find blockchain technology providing transparency for the food supply chain, securing healthcare data, finances, assets, retail, innovating gaming and overall changing how we handle data and ownership on a large scale.
How the BLOCKCHAIN Works.
For proof-of-work blockchains, this technology consists of three important concepts: blocks, nodes and miners.
THE BLOCK EXPLAINED
Every chain consists of multiple blocks and each block has three basic elements:
-
The data in the block.
-
The nonce — “number used only once.” A nonce in blockchain is a whole number that’s randomly generated when a block is created, which then generates a block header hash.
-
The hash — a hash in blockchain is a number permanently attached to the nonce. For Bitcoin hashes, these values must start with a huge number of zeroes (i.e., be extremely small).
When the first block of a chain is created, a nonce generates the cryptographic hash. The data in the block is considered signed and forever tied to the nonce and hash unless it is mined.
BLOCKCHAIN APPLICATION
Blockchain isn’t only used for financial transactions. Due to its secure and transparent nature, the technology is versatile to needs beyond one area of expertise. Industries covering energy, logistics, education and more are utilizing the benefits of blockchain every day.
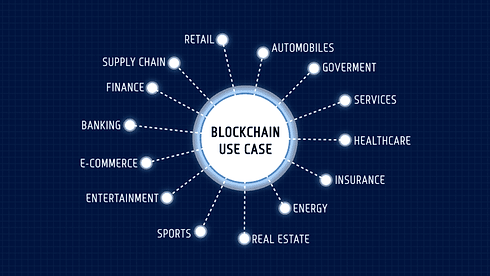
TOP BLOCKCHAIN USES...
-
Cryptocurrency
-
Cybersecurity
-
Accounting and Record Keeping
-
Supply Chain
-
Healthcare
BLOCKCHAIN PLATFORM
While a blockchain network describes the distributed ledger infrastructure, a blockchain platform describes a medium where users can interact with a blockchain and its network. Blockchain platforms are created to be scalable and act as extensions from an existing blockchain infrastructure, allowing information exchange and services to be powered directly from this framework.
An example of a blockchain platform includes Ethereum, a software platform which houses the Etherium, or ether, cryptocurrency. With the Ethereum platform, users can also create programmable tokens and smart contracts which are built directly upon the Ethereum blockchain infrastructure.

BLOCKCHAIN MINING
Miners create new blocks on the chain through a process called mining.
In a blockchain every block has its own unique nonce and hash, but also references the hash of the previous block in the chain, so mining a block isn't easy, especially on large chains.
Miners use special software to solve the incredibly complex math problem of finding a nonce that generates an accepted hash. Because the nonce is only 32 bits and the hash is 256, there are roughly four billion possible nonce-hash combinations that must be mined before the right one is found. When that happens miners are said to have found the "golden nonce" and their block is added to the chain.
Making a change to any block earlier in the chain requires re-mining not just the block with the change, but all of the blocks that come after. This is why it's extremely difficult to manipulate blockchain technology. Think of it as "safety in math" since finding golden nonces requires an enormous amount of time and computing power.
When a block is successfully mined, the change is accepted by all of the nodes on the network and the miner is rewarded financially.
Decentralization in Blockchain
One of the most important concepts in blockchain technology is decentralization. No one computer or organization can own the chain. Instead, it is a distributed ledger via the nodes connected to the chain. Blockchain nodes can be any kind of electronic device that maintains copies of the chain and keeps the network functioning.
Every node has its own copy of the blockchain and the network must algorithmically approve any newly mined block for the chain to be updated, trusted and verified. Since blockchains are transparent, every action in the ledger can be easily checked and viewed, creating inherent blockchain security. Each participant is given a unique alphanumeric identification number that shows their transactions.
Combining public information with a system of checks-and-balances helps the blockchain maintain integrity and creates trust among users. Essentially, blockchains can be thought of as the scalability of trust via technology.
